Pronouns
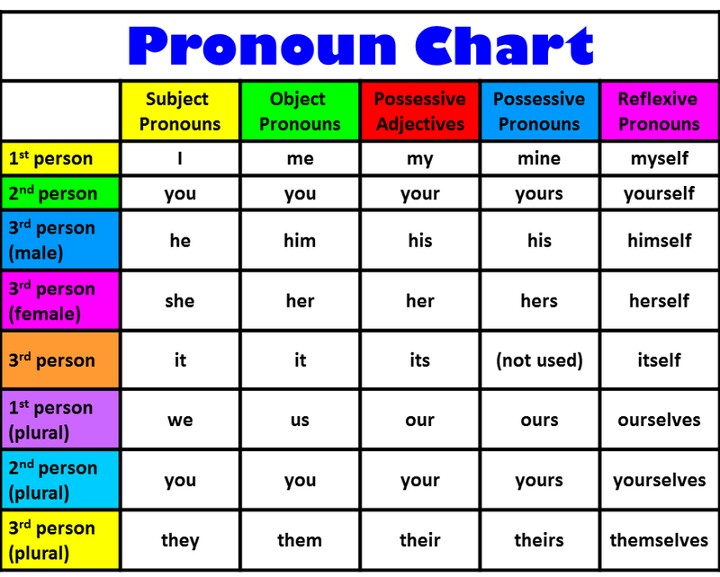
A pronoun is defined as a word that may be substituted for a noun. Pronouns make up a small subcategory of nouns. The distinguishing characteristic of pronouns is that they can be substituted for other nouns.
A pronoun is a word that replaces a noun in a sentence. Pronouns are used so that our language is not cumbersome with the same nouns being repeated over and over in a paragraph.

Types of Pronouns
Pronouns can be divided into numerous categories including:

Pronoun Rules
There are a few important rules for using pronouns. As you read through these rules and the examples in the next section, notice how the pronoun rules are followed. Soon you’ll see that pronouns are easy to work with.

A pronoun is used in place of a noun that has already been mentioned or that is already known, often to avoid repeating the noun. For example, Kate was tired so she went to bed.
Michael took the children with him.
Kieran’s face was close to mine.
That is a good idea.
Anything might happen.
Noun
A noun is a word that names something: either a person, place, or thing. In a sentence, nouns can play the role of subject, direct object, indirect object, subject complement, object complement, appositive, or adjective.
A noun is a word that identifies a person (name), animal, place, thing, or idea.

There are several different types of noun, as follows:
Common noun
Proper noun
Concrete noun
Abstract noun
Collective noun
A common noun is a noun that refers to people or things in general, e.g. boy, country, bridge, city, birth, day, happiness.
A proper noun is a name that identifies a particular person, place, or thing, e.g. Steven, Africa, London, Monday. In written English, proper nouns begin with capital letters.
A concrete noun is a noun which refers to people and to things that exist physically and can be seen, touched, smelled, heard or tasted. Examples include dog, building, coffee, tree, rain, beach, tune.
An abstract noun is a noun which refers to ideas, qualities, and conditions - things that cannot be seen or touched and things which have no physical reality, e.g. truth, danger, happiness, time, friendship, humor.
Collective nouns refer to groups of people or things, e.g. audience, family, government, team, jury. In American English, most collective nouns are treated as singular, with a singular verb:
The whole family was at the table.
In British English, the preceding sentence would be correct, but it would also be correct to treat the collective noun as a plural, with a plural verb:
A noun may belong to more than one category. For example, happiness is both a common noun and an abstract noun, while Mount Everest is both a concrete noun and a proper noun.

Recap
Q.1 |
Select the correct one word substitution for the given sentence. One who is out to destroy all governance, law and order |
| a) | Alchemist |
| b) | Altruist |
| c) | Attorney |
| d) | Anarchist |
Q.2 |
Select the correct one word substitution for the given sentence. To pronounce not guilty of criminal charges |
| a) | Exonerate |
| b) | Etching |
| c) | Epicure |
| d) | Ecology |
Q.3 |
Select the correct one word substitution for the given sentence. Having a chance of occurring too low to inspire belief |
| a) | Imperative |
| b) | Impervious |
| c) | Improbable |
| d) | Incredible |
Q.4 |
Select the correct one word substitution for the given sentence. Sleep inducing |
| a) | Translucent |
| b) | Transcending |
| c) | Sinecure |
| d) | Sedative |
Q.5 |
Select the correct one word substitution for the given sentence. A person appointed or elected to represent others |
| a) | Judge |
| b) | Jury |
| c) | Delegate |
| d) | Associate |
Q.6 |
Select the correct one word substitution for the given sentence. Rules governing socially acceptable behaviour |
| a) | Eulogy |
| b) | Etiquette |
| c) | Etymology |
| d) | Epidemic |
Q.7 |
Select the correct one word substitution for the given sentence. Someone who dislikes people in general |
| a) | Mediocre |
| b) | Philanthropist |
| c) | Misogynist |
| d) | Misanthrope |
Q.8 |
Select the correct one word substitution for the given sentence. Suitable for drinking |
| a) | Potable |
| b) | Drinkable |
| c) | Pauper |
| d) | Panacea |
Q.9 |
Select the correct one word substitution for the given sentence. Seeming unaffected by pleasure or pain |
| a) | Stagnant |
| b) | Stoic |
| c) | Predator |
| d) | Epicurean |
Q.10 |
Arrangements of events according to dates or times of occurance. |
| a) | epilogue |
| b) | chronology |
| c) | coalesce |
| d) | centipede |
Your Score: 0/10
Yearlong program for Olympiads preparation & to build necessary skills for future.
Explore More
Time to mark your calendar with the upcoming Olympiads exam schedule.
Explore More
Take your Olympiad preparation to next-level by taking LIVE Classes.
Explore More
Assess your performance by taking topic-wise and full length mock tests.
Explore More
Online tuitions for international compeitions like SASMO, SEAMO, etc for Grades 1-11.
Explore More