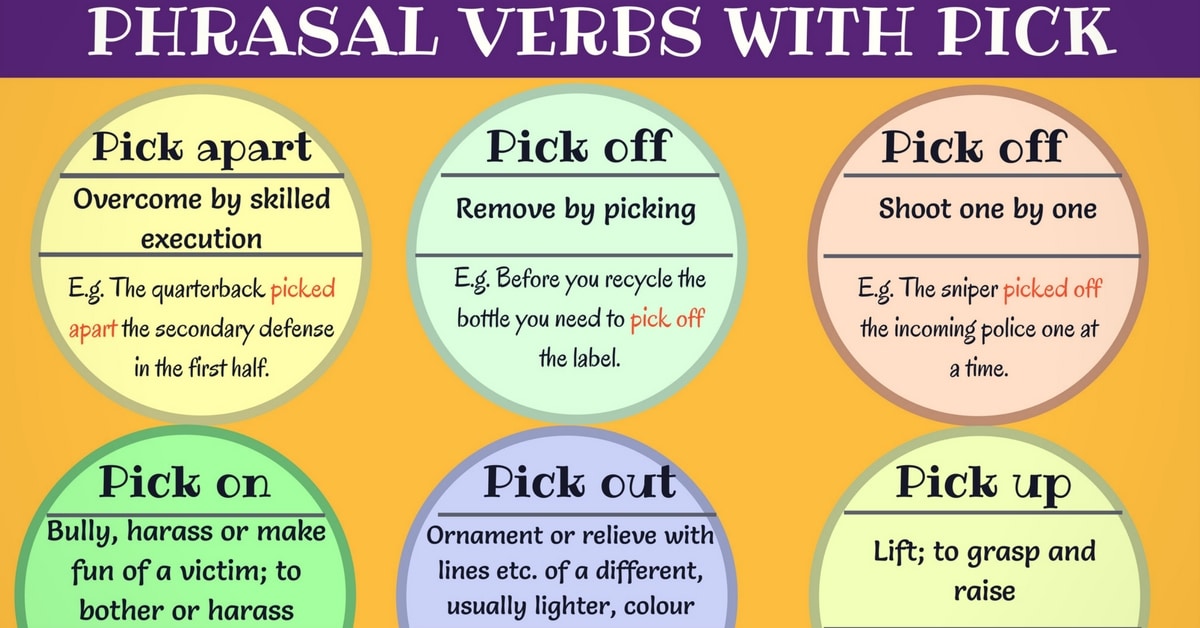
Phrasal Verbs
A phrasal verb is a verb that is made up of the main verb together with an adverb or a preposition, or both. Generally, their meaning is not obvious from the meanings of the individual words themselves. A phrasal verb is a combination of a verb + a preposition or verb +adverb that when used together, usually take on a different meaning to that of the original verb.


For instance, in the first example, the phrasal verb ‘to look down on someone’ doesn’t mean that you are looking down from a higher place at someone who is below you; it means that you think that you are better than someone.

Transitivity
Phrasal verbs can be Intransitive: We broke up two years ago.
They set off early to miss the traffic.
He pulled up outside the cottage.
Transitive: The police were called to break up the fight.
When the door is opened, it sets off an alarm.
They pulled the house down and redeveloped the site.
A phrasal verb is a phrase that’s made up of a verb and another word or two, usually a preposition but sometimes an adverb. Phrasal verbs work by changing the verb’s meaning based on the preposition that follows them.
It’s easier than you think you probably already know a number of phrasal verbs. For example: Come on, let’s learn some phrasal verbs. The words “come on" in that sentence are a phrasal verb!
Phrasal verb examples:
Idioms
Every language has its own collection of wise sayings. They offer advice about how to live and also transfer some underlying ideas, principles and values of a given culture/society. These sayings are called "idioms". There are some of the commonly used idioms and sayings can help to speak English by learning English idiomatic expressions.
An idiom is a phrase, saying or a group of words that has a metaphorical meaning, which has become accepted in common usage. An idiom’s symbolic sense is quite different from the literal meaning or definition of the words of which it is made. There are a large number of Idioms and they are used very commonly in all languages.

Idioms, in fact, evolve the language; they are the building blocks of a language and civilization. They also have a great intensity to make a language interesting and dynamic.
They provide interesting insights into the use of words, languages and the thought processes of their speakers. They have a sense of mystery and fun about them.
piece of cake
Meaning: something that is easy to do.
Example: Making spaghetti Bolognese is a piece of cake.
Meaning: a controversial issue or situation that is awkward or unpleasant to deal with.
Example: The subject of bullying and fighting in my school is a hot potato.
Meaning: very rarely.
Example: I go to visit my grandfather only once in a blue moon; he lives in a remote farmhouse.
Meaning: easy option.
Example: Taking care of my younger sister is no bed of roses; she is very silly
Modals
A modal is a type of auxiliary verb that is used to express: ability, possibility, permission or obligation. Modal phrases are used to express the same things as modals but are a combination of auxiliary verbs and the preposition to. The modals and semi-modals in English are:
Modals are special verbs which behave irregularly in English. They are different from normal verbs like "work, play, visit..." They give additional information about the function of the main verb that follows it. They have a great variety of communicative functions.

Here are some characteristics of modal verbs:
Examples of Modal Verbs
Can, could, may, might, will, would, shall, should, must.
We use modal verbs to show if we believe something is certain, probable or possible. We also use modals to do things like talking about ability, asking permission making requests and offers, and so on. The modal verbs include can, must, may, might, will, would, should. They are used with other verbs to express ability, obligation, possibility, and so on.

Word order
Word order refers to the way words are arranged in a sentence. The standard word order in English is Subject + Verb + Object. To determine the proper sequence of words, you need to understand what the subject, verb and object(s) are.

The sequence of words is critical when communicating in English because it can impact the meaning of what you’re trying to say. The sentence, “The chicken crossed the road" and “The road crossed the chicken" take on two different meanings because the subject and object are inverted. The same would be true if the verb was used out of order, for example: “Crossed the road the chicken."
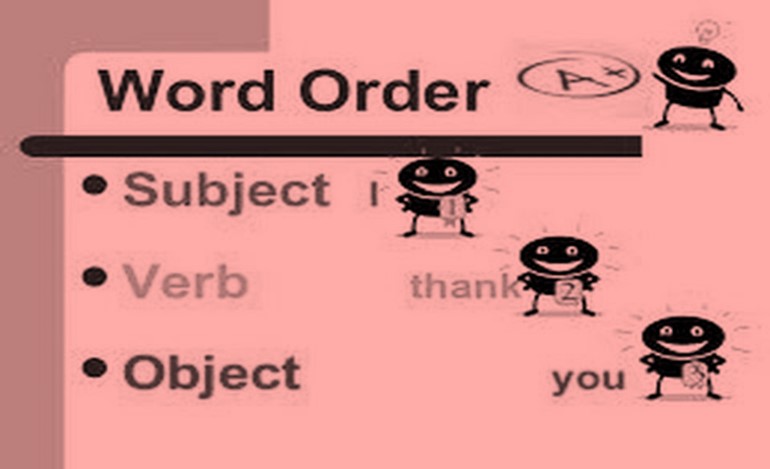
Word order is important: it’s what makes your sentences make sense! So, proper word order is an essential part of writing and speaking when we put words in the wrong order, the result is a confusing, and an incorrect sentence.
In English, we follow one main pattern for normal sentences and one main pattern for sentences that ask a question.
A sentence’s standard word order is Subject + Verb + Object (SVO). Remember, the subject is what a sentence is about; so, it comes first. For example:
The dog (subject) + eats (verb) + popcorn (object).
The subject comes first in a sentence because it makes our meaning clear when writing and speaking. Then, the verb comes after the subject, and the object comes after the verb; and that’s the most common word order. Otherwise, a sentence doesn’t make sense, like this:
Eats popcorn the dog. (verb + object + subject)
Popcorn the dog eats. (object + subject + verb)
Recap
Be sure to put on a life jacket before getting into the boat.
We left out the trash for pickup.
Q.1 |
Fill in the blanks by selecting the correct phrasal verb. When we got ________ to the room, she had already left. |
| a) | through |
| b) | away |
| c) | back |
| d) | together |
Q.2 |
Fill in the blanks by selecting the correct phrasal verb. We have to get _________ for our presentation on Friday. |
| a) | away |
| b) | together |
| c) | out |
| d) | in |
Q.3 |
Fill in the blanks by selecting the correct phrasal verb. They got _________ the bus and walked to school. |
| a) | back |
| b) | in |
| c) | off |
| d) | up |
Q.4 |
Fill in the blanks by selecting the correct phrasal verb. Students have to get __________ when the teacher comes in. |
| a) | down |
| b) | away |
| c) | out |
| d) | up |
Q.5 |
Fill in the blanks by selecting the correct phrasal verb. Our plane is getting _______now. |
| a) | through |
| b) | in |
| c) | off |
| d) | away |
Q.6 |
Fill in the blanks by selecting the correct phrasal verb. Does Ken get ___________ with his parents? |
| a) | along |
| b) | away |
| c) | in |
| d) | through |
Q.7 |
Fill in the blanks by selecting the correct phrasal verb. We couldn't get ________ the bus because it didn't stop at our station. |
| a) | through |
| b) | up |
| c) | away |
| d) | in |
Q.8 |
Fill in the blanks by selecting the correct phrasal verb. The police let him get _________ with only a $10 ticket. |
| a) | away |
| b) | through |
| c) | together |
| d) | up |
Q.9 |
Fill in the blanks by selecting the correct phrasal verb. How do you feel when you look _________ your childhood? |
| a) | in to |
| b) | away |
| c) | back to |
| d) | back up |
Q.10 |
Fill in the blanks by selecting the correct phrasal verb. Our boss looks __________ on some people in his firm. |
| a) | through |
| b) | down |
| c) | up |
| d) | into |
Your Score: 0/10
Yearlong program for Olympiads preparation & to build necessary skills for future.
Explore More
Time to mark your calendar with the upcoming Olympiads exam schedule.
Explore More
Take your Olympiad preparation to next-level by taking LIVE Classes.
Explore More
Assess your performance by taking topic-wise and full length mock tests.
Explore More
Online tuitions for international compeitions like SASMO, SEAMO, etc for Grades 1-11.
Explore More